Cardiomyopathy
DEFINITION
Peyakit cardiomyopathy is a progressive disorder that causes changes in structure or function disturbance in the muscle wall of the lower heart chambers (ventricles).
There are three forms of cardiomyopathy:
Dilated congestive cardiomyopathy
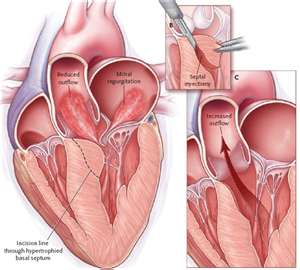
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Restrictive cardiomyopathy.
CAUSE
The cause of cardiomyopathy can be a variety of diseases that have known or could have unknown causes.
SYMPTOMS
Some patients may not experience symptoms or signs of cardiomyopathy in the early stages of disease cardiomyopathy. But in line with the development of cardiomyopathy disease, cardiomyopathy symptoms and signs usually appear.
Signs or symptoms of cardiomyopathy typically include:
Running out of breath during exertion or even while resting.
Swelling of the feet and ankles.
Flatulence contains water.
Feeling tired.
Irregular heartbeat is felt quickly, shaking and palpitations.
Dizziness, lightheadedness and fainting.
Cardiomyopathy of any kind if not treated, the symptoms will worsen. In certain patients with signs and symptoms of cardiomyopathy rapidly deteriorating, while others do not worsen the long view of time.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will perform a physical examination, checking personal and family medical history, and ask when your symptoms appear, such as: whether the exercise causes symptoms. If your doctor thinks you have cardiomyopathy, you may need to undergo some tests to confirm the diagnosis.
These tests include:
Chest X-ray. Does your heart will show the image enlarged.
Echocardiogram. Echocardiogram uses sound waves to produce images of the heart. Your doctor may use these images to examine the size and movements such as the beating heart.
Electrocardiogram (ECG). In this noninvasive test, electrode patches attached to your skin to measure electrical impulses from your heart. ECG can show disturbances in the electrical activity of your heart, which can detect abnormal heart rhythms and the area of injury.
Cardiac catheterization and biopsy. In this procedure, a small tube (catheter) is inserted in the groin and through blood vessels to the heart, where a small sample (biopsy) from your heart can be extracted for analysis in the laboratory. The pressure in the ventricle can be measured to see how strong the blood pumping through your heart. Images of the heart arteries can be taken during the procedure (coronary angiogram) to ensure that your heart there is no blockage.
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Cardiac MRI is the imaging technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create images of your heart. Cardiac MRI is often used in addition to echocardiography, especially if the image of your echocardiogram does not help in making a diagnosis.
Blood tests. A blood test can measure the B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), a protein that is produced in your heart. BNP levels in your blood increases when heart you depressed because of heart failure, complications that occur in cardiomyopathy.
Various other blood tests can be done, including to check kidney function and found anemia and thyroid problems. Your iron level can be measured. Having too much can indicate iron overload disorder called hemochromatosis. Iron that accumulates in your heart too much can weaken the heart muscle and causes cardiomyopathy.
PREVENTION
In most cases you can not prevent cardiomyopathy. Berritahu your doctor if you have a family history of conditions. If cardiomyopathy is diagnosed early, treatment can prevent worsening of disease.
You can help reduce kesmungkinan for heart failure by avoiding some conditions that can contribute to a weak heart, including the abuse of alcohol or cocaine, or not getting enough vitamins and minerals. Controlling high blood pressure with diet and exercise also prevents heart failure in later life.
Friday, October 28, 2011
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
michael kors handbags
ReplyDeletenike trainers
armani exchange
new balance outlet
nike store
nike huarache trainers
skechers shoes
ecco
coach outlet
nike free 5