Appendix Definition
Acute appendicitis is the most common cause of acute inflammation on the bottom right quadrant abdominal cavity, the most common cause for emergency abdominal surgery (Smeltzer, 2001).
Appendicitis is a condition in which the infection occurs in the appendix. In mild cases may recover without treatment, but many cases require laparotomy with removal of an infected appendix. If untreated, mortality is high, due to peritonitis and shock when an infected appendix destroyed. (Anonymous, Appendicitis, 2007)
Appendicitis is the inflammation due to infection of the appendix or the appendix (appendix). These infections can lead to pus. If the infection worsens, the appendix can rupture. The appendix is an intestinal tract clogged and prominent edges from the beginning of the colon or cecum (cecum). Appendix magnitude around the little finger and the hand is located in the lower right abdomen. The structure is like other parts of the intestine. However, the mucus glands that always contains a lot of mucus. (Anonymous, Appendicitis, 2007)
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix / appendix (Anonymous, Appendicitis, 2007)
Classification
Classification appendicitis divided into 2 ie:
Acute appendicitis, divided into: acute appendicitis or segmentalis fokalis, ie after recovery will occur locally stricture. Appendicitis purulenta diffusion, which have accumulated pus.
Chronic appendicitis, divided into: chronic appendicitis fokalis or partially, after recovering stricture will occur locally. Chronic appendicitis appendix obliteritiva is tilted, usually found in old age.
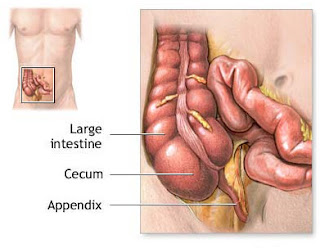
Anatomy and Physiology Appendix is a small, vestigial organs (organs that do not work) is attached to a third finger.
Location of the appendix.
Appendix located at the tip of the sacrum from approximately 2 cm below the anterior ileo saekum, empties into the posterior and medial part of saekum. At the third meeting taenia namely: taenia anterior, medial and posterior. The clinic is located in the area Mc appendix. Burney is the third center line connecting the center-right Messiah.
The size and contents of the appendix.
Average appendix length 6-9 cm. Width 0.3 to 0.7 cm. Contents 0.1 cc, liquid containing alkaline amylase and mucin.
The position of the appendix.
Laterosekal: lateral to the ascending colon. In the inguinal region: veer toward the abdominal wall. Pelvis minor.
Etiology
The occurrence of acute appendicitis is generally caused by bacterial infection. But there are many factors trigger the disease. Among obstruction that occurs in the lumen of the appendix. Obstruction of the lumen of the appendix is usually caused due to a heap of hard stools (fekalit), hipeplasia lymphoid tissue, worm diseases, parasites, foreign bodies in the body, the primary cancer and stricture. However, the most frequent cause luminal obstruction are fekalit appendix and lymphoid tissue hyperplasia. (Irga, 2007)
Pathophysiology
Appendix terinflamasi and experienced edema as a result of bent or blocked possibly by fekolit (hard mass of faeces) or foreign bodies. The process of inflammation increased intraluminal pressure, causing upper abdominal pain or severe spread progressively, in a few hours localized in the lower right quadrant of the abdomen. Finally, the appendix which contains terinflamasi pussy.
Clinical manifestations
Appendicitis has a typical combination of symptoms, which consist of: Nausea, vomiting and severe pain in the lower right abdomen. Pain may be sudden starts in the upper abdomen or around the navel, then nausea and vomiting. After several hours, the nausea disappeared and the pain moves to the lower right abdomen. If the doctor presses on this area, the patient felt dull pain and if this pressure is released, the pain can increase sharply. Fever may reach 37.8 to 38.8 ° Celsius.
In infants and children, the pain is a thorough, in all parts of the stomach. In the elderly and pregnant women, the pain is not too heavy and in this area tumpulnya pain is not too pronounced. If the appendix ruptured, pain and fever can be severe. Infection that gets worse can cause shock. (Anonymous, Appendicitis, 2007)
Diagnostic tests
To establish the diagnosis of appendicitis based on anamnese coupled with laboratory and other investigation.
Symptoms of appendicitis is confirmed by anamnese, there are 4 important things are: Pain at first in epigastrium (visceral pain), which later spread to the lower right abdomen. Vomiting due to visceral pain. Heat (because germs that live in the intestinal wall).
Other symptoms are the body weak and poor appetite, the patient appeared ill, avoid movement, in the stomach ache.
Localisation another examination.
If perforation has occurred, the pain will occur in the entire stomach, but most felt pain in the area Mc point. Burney. If it infiltrates, local infection can also occur if the person in pain, and we're going to feel like there is tumor at the point of Mc. Burney.
Test rectal.
In the toucher rectal examination will be palpable lump and the patient felt pain in the area prolitotomi.
Laboratory tests Leukocytes increased as a physiological response to protect the body against microorganisms that attack.
In acute appendicitis and perforation will occur lekositosis higher again. Hb (hemoglobin) appeared normal. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) was increased on the state of appendicitis infiltrates. Urine routine is important to see what there is infection in the kidney. In the photo is not radiological examination can help to diagnose acute appendicitis, except in case of peritonitis, but sometimes a picture can be found as follows: There is little fluid levels due to the air and fluid. Sometimes there are fecolit (blockage). In the state of perforation were found free air in the diaphragm.
Management
Surgery is indicated when the diagnosis of appendicitis has been enforced. Antibiotics and IV fluids given to surgery. analgesics can be given after the diagnosis is established. Apendektomi (surgery to remove the appendix) is done as soon as possible to reduce the risk of perforation.
Apendektomi can be performed under general or spinal anesthesia with a lower abdominal incision or by laparoscopy, which is the latest method is very effective. Nursing Concepts Before surgery is performed the client needs to be prepared physically and psychologically, in addition to the client also needs to be given the knowledge of the events that will be experienced after surgery and given physical exercises (deep breathing, leg movement and sitting) for use in post operative period. This is important because many clients feel anxious or worried when to operate and also to the acceptance of anesthesia.
To complement this, the nurse in the conduct of nursing care should use the following steps:
Assessment
The identity of the client's name, age, sex, marital status, religion, tribe / nation, education, occupation, income, address and registration number.
The identity of the person in the health history now.
The main complaint the Client will get around epigastric pain radiating to the lower right abdomen. Complaints arise right lower abdominal pain may be a few hours later after the pain in the center or at the epigastric be felt in some time ago.
Nature of complaint Pain is felt constantly, can be lost or there is pain in a long time. Complaints that accompany the client usually complain of nausea and vomiting, hot. Past medical history is usually associated with health problems clients present state of general physical examination looks sick Clients mild / moderate / severe.
As an indicator of body weight to determine the administration of drugs.
Circulation: Clients may tachycardia. Respiration: Takipnoe, shallow breathing. Activity / rest: Depression. Eliminate Constipation in early awitan, sometimes diarrhea. Abdominal distension, tenderness / pain off, stiffness, decreased or absent bowel sounds.
Pain / comfort Abdominal pain around the epigastrium and umbilicus, which increases weight and localized at the point of Mc. Burney, increased by walking, sneezing, coughing or breathing deeply. Pain in the lower right quadrant because the position of the right leg extension / upright sitting position.
Security Fever, usually low.
Client psychological data seem nervous.
There are changes in pulse and respiration. There is a feeling of fear. Appearances are not quiet.
Nursing Diagnosis
Risk reduction in fluid volume associated with the nausea and vomiting.
The risk of infection associated with an inadequate defense.
Pain associated with distention of intestinal tissue.
Lack of knowledge about the disease process associated with less information.
Nutrition is less than the needs associated with decreased intake.
Self-care deficit related to the perceived weakness
Nursing intervention.
Plan objectives and interventions tailored to the diagnosis and prioritization of nursing.
The risk of lack of fluid volume associated with a sense of nausea and vomiting, marked by: Sometimes diarrhea. Abdominal distension. Tense. Decreased appetite. There is a feeling of nausea and vomiting. Objective: To maintain a balance of fluid volume with criteria: Client is not diarrhea. Good appetite. Clients no nausea and vomiting.
Interventions: Monitor vital signs.
Rational: It is an early indicator of hypovolemia.
Monitor intake and urine output and concentration.
Rational: The reduced urine output and concentration will increase the sensitivity / sediment as one the impression of dehydration and require increased fluids.
Give fluid little by little but often.
Rationale: To minimize loss of fluid.
The risk of infection associated with an inadequate defense, characterized by: body temperature above normal. Respiratory frequency increases. Abdominal distension. Mc-tender point areas. Burney Leuco> 10.000/mm3 Objective: There will be an infection with the criteria: no signs of infection post-operative (no longer heat, redness).
Intervention: Clean field operations from several organisms that may exist through the principles of shaving.
Rationale: Measurement in the opposite direction of hair growth will reach to the bottom of the hair, so it really clean to avoid the growth of micro organisms.
Give laxatives the day before surgery and by doing klisma.
Rational: Laxatives can stimulate intestinal peristaltic so the chapter can be smoothly. While klisma to stimulate peristaltic higher, so that it can lead to rupture of the appendix.
Encourage clients with the perfect shower.
Rational: The skin is clean has great significance to the emergence of micro-organisms.
HE about the importance of personal hygiene clients.
Rational: With the understanding of the client, the client can work together in the implementation of the action.
Impaired sense of comfort pain associated with distention of intestinal tissue, characterized by: Breathing tachipnea. Circulation tachicardia. Pain in the area spreading to the region epigastrum Mc. Burney Fidget. The client complained of pain in the lower right abdomen.
Objective: The pain will be overcome with criteria: normal breathing. Normal circulation.
Intervention: Assess the level of pain, pain location and characteristics.
Rational: To determine the extent of pain and is an indicator of early to be able to provide follow-up.
Encourage deep breathing.
Rational: breathing in O2 to breathe adequately so that the muscles into relaxation so as to reduce pain.
Do the gate control.
Rational: With the gate control of large-diameter nerve stimulates the nerves of small diameter so that the stimulus of pain is not transmitted to the hypothalamus.
Give analgesics.
Rational: As a prophylactic in order to relieve pain (if already know the symptoms of certain).
Lack of knowledge about the disease process associated with less information. Fidget. Glum face. Clients often ask about the disease. Clients complain of pain. Clients complain of difficulty sleeping
Objective: The client will understand the benefits of post-operative care and treatment.
Intervention: Explain to clients about exercises that will be used after surgery.
Rationale: The client can understand and can plan and to implement after the surgery, so it can restore optimal function organs.
Encourage activities that progressive and patient with periods of rest after surgery.
Rationale: Preventing bedsores and to accelerate healing.
Discuss hygiene verband incision covering turnover, restrictions on bathing, and healing exercises.
Rational: Understand and are willing to work together through traumatic can accelerate the healing process.
Nutrition is less than the needs associated with decreased intake. Decreased appetite Weight loss is not spent Meal There is a sense of nausea vomiting
Objective: The client capable of taking care of yourself
Intervention: Assess the extent to which nutrients inaccuracies client
Rational: to analyze the cause of implementing the intervention.
Estimate / calculate the calorie intake, keep the comments about your appetite until at least
Rationale: Identify deficiencies / needs nutrition focuses on the problem of making a negative atmosphere and affect the input.
Weigh weight as indicated
Rational: Monitors the effectiveness of the diet.
Give eat little but often
Rational: It gives a sense of boredom and nutrient intake can be improved.
Encourage oral hygiene before meals
Rational: The mouth of the net increase appetite
Offer a drink at dinner when tolerant.
Rational: It can reduce nausea and eliminate gas.
Consul's favorite neighbor / dislikes of patients who causes distress.
Rational: Involving patients in planning, enabling the patient to have a sense of control and encouraged to eat.
Give a varied diet
Rational: Foods that can increase appetite varied clients.
Self-care deficit related to a perceived weakness. Fingernail dirty look dirty scalp looks dirty Clients
Objective: The client capable of taking care of yourself
Intervention: Bathe the patient every day until the client is able to implement their own as well as washing client's hair and cut nails.
Rational: In order for a fresh body, blood circulation and improve health.
Replace dirty clothes with a clean.
Rational: To protect the client from germs and increase comfort
HE give to clients and their families about the importance of personal hygiene.
Rational: In order for clients and families can be motivated to maintain personal hygiene.
Give praise to the client about cleanliness.
Rational: In order for clients to feel flattered and more cooperative in cleanliness
Guided family / wife bathe clients
Rational: In order to apply the skills
Clean and adjust the bed position and client.
Rationale: Clients feel comfortable with weaving a clean and prevent infection.
Implementation
Execution is the actual provision of nursing care in the form of a systematic series of activities based on planning to achieve optimal results. At this stage the nurse to use all capabilities in carrying out action against client nursing in general and specifically on the client post apendektomi. In this implementation nurses perform its functions independently, interdependent and dependent.
In the independent functions are included from all activities initiated by the nurses themselves in accordance with their capabilities and skills of its On interdependent functions is where the function performed by cooperating with the professions / disciplines in nursing and other health services, while the dependent function is a function conducted by nurses based on the message to others.
Monday, May 30, 2011
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
Thanks a lot for providing the amazing info is visible about appendix pain The main symptom of appendix is abdominal pain.
ReplyDeleteIt's a great post that provide complete information regarding cancer and treatment also.
ReplyDeleteBrain Cancer Treatment
yeezy boost
ReplyDeletecalvin klein outlet online
curry shoes
air max
nike air force 1
golden goose starter
coach outlet
balenciaga shoes
michael kors outlet
caterpillar shoes